For days 3-4 of the Cloud Challenge, we were asked to learn about Amazon EC2 instances. Topics we were expected to learn include: the types of EC2 instances, their pricing options, and their use cases. We were also asked to learn about regions and availability zones.
Before diving into EC2 instances, let me first define the terms region and availability zone.
A region is a physical location around the world where data centers are clustered together. An availability zone is a zoned area within a region that houses one or more data centers. This approach was designed to ensure that applications and databases are highly available, fault tolerant, and scalable.
The photo below, taken from the Tutorials Dojo website, is a diagram of region and availability zones.
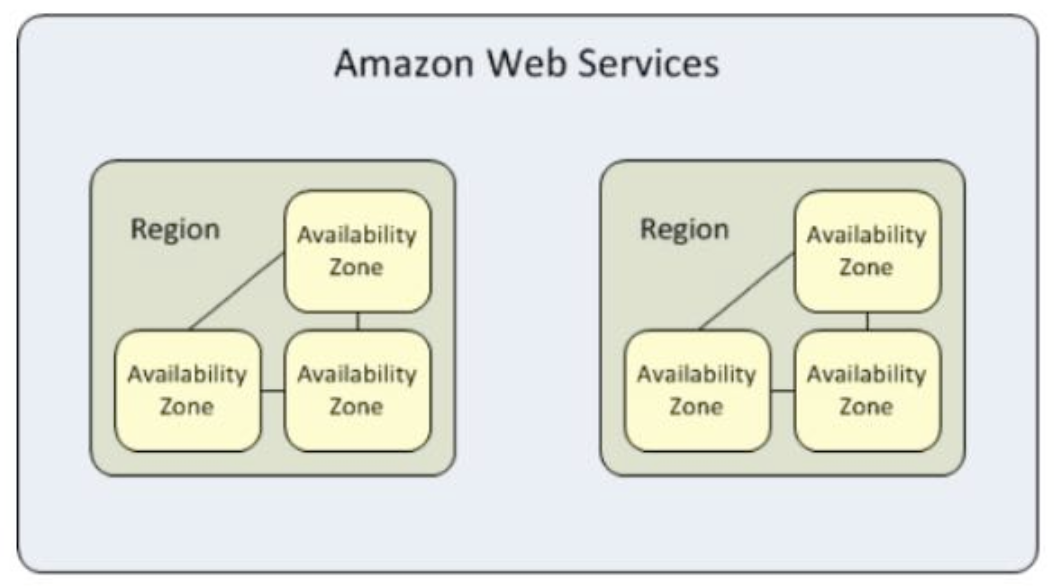
Now that I know what regions and availability zones are, I then moved on to learn about EC2 instances.
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is a core compute service that runs virtual servers in the cloud. It allows users to launch virtual machines to host and manage their applications no matter where they are in the world. The benefits of EC2 are that it’s reliable, easy to scale, integrates with other AWS services, and you only pay for what you use.
There are five types of EC2 instances:
General Purpose: A general purpose instance can be used for a wide variety of workloads. They provides a balance of compute, networking, and memory resources.
Compute Optimized: A compute optimized instance is used for applications that require a lot of computation can benefit from high-performance CPUs.
Memory Optimized: Memory optimized instances are for workloads that process large data sets in memory.
Accelerated Computing: Uses hardware accelerators to perform tasks such as graphics processing more efficiently than software running on CPUs.
Storage Optimized: Storage optimized instances are used for workloads that require high, sequential read and write access to large data sets.
Amazon EC2 offers multiple options for users to purchase computing resources that fit their needs.
The seven types of purchasing options are:
On-Demand Instances: Pay by the hour or second for instances that launch.
Savings Plans: Reduce EC2 costs by committing to a consistent amount of usage,in USD per hour, for a term of 1 or 3 years.
Reserved Instances: Reduce Amazon EC2 costs by committing to a consistent instance configuration, including instance type and region, for a term of 1 or 3 years.
Spot Instances: Reduce Amazon EC2 costs significantly by requesting unused EC2 instances.
Dedicated Hosts: Pay for a physical host that is fully dedicated to running your instances, and bring your existing per-socket, per-core, or per-VM software licenses to reduce costs.
Dedicated Instances: Pay by the hour for instances that run on single-tenant hardware.
Capacity Reservations: Reserve capacity for EC2 instances in a specific availability zone.
Lastly, Amazon EC2 has a service called Auto Scaling which helps ensure that a user has the right number of EC2 instances available to handle the load of their applications.
Additional Resources:
Tiny Technical Tutorials on YouTube